1.2 Trillion compounds in HitGen's DNA-encoded chemical libraries, for your innovative drug discovery
DNA Encoded Library Design
In the realm of innovative drug development, the most crucial and pivotal step is the discovery of small molecules capable of binding to biological targets and eliciting a pharmacological effect. Consequently, the design of compound libraries for biological screening is of paramount importance for the identification of high-quality hit compounds and lead compounds. Since the advent of DNA-encoded compound library technology, it has evolved into a formidable tool for novel drug discovery, capable of generating hundreds of billions to trillions of new molecules for drug development. Over the years, HitGen has explored and summarized the design strategies for DNA-encoded compound libraries, taking into account both chemistry-driven and biology-driven approaches, as well as considering the control of physicochemical properties to ensure that the library molecules are more "drug-like" overall.
Chemistry Driven Force:
· HitGen has developed over 150 DNA-compatible chemical reactions to construct diverse drug-like encoded molecules.
· HitGen has designed and synthesized thousands of unique scaffolds and building blocks to achieve compound novelty.
Biology Driven Force:
· HitGen continuously tracks cutting-edge drug molecule types, encompassing and expanding the potential chemical space. This includes covering existing drugs, molecules in clinical trials, preclinical active molecules, and actively utilizing privileged structures to construct compound libraries.
· HitGen designs and constructs compound libraries based on specific structural information of a certain class or individual biological targets, enabling rapid expansion and optimization of potential molecules.
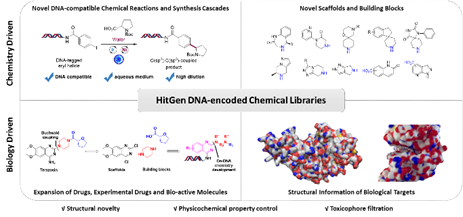
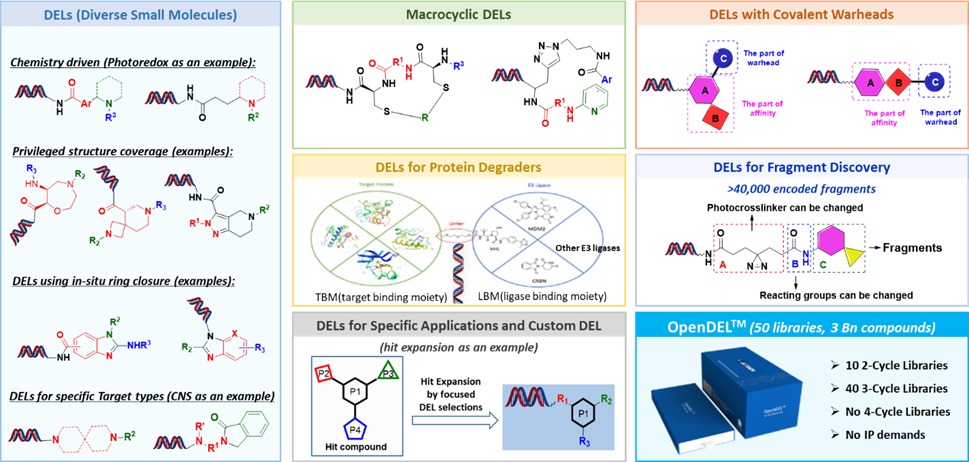
Driven by the principles of biological and chemical design, HitGen has constructed a diverse array of DNA-encoded libraries (DELs), including traditional small molecule DELs, macrocyclic peptide DELs, covalent DELs, protein degradation DELs, fragment DELs, and focused DELs, collectively encompassing over 1.2 trillion molecular entities. Additionally, HitGen has built a 3-billion-member OpenDEL library, offering flexible service models to cater to the diverse needs of different client groups.)
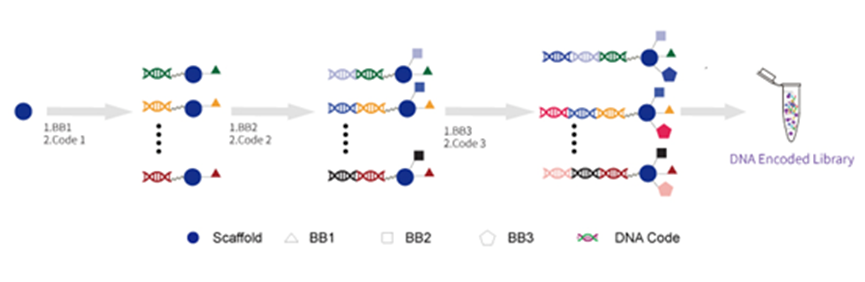
DNA Encoded Library Synthesis:
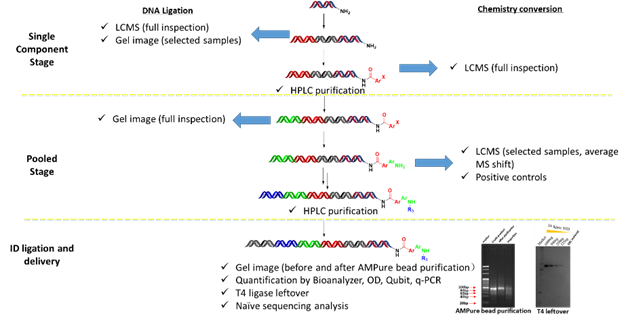
Over the past two decades, DNA-encoded library (DEL) technology has been revolutionizing the field of small molecule drug discovery. This technology enables the synthesis and screening of hundreds of billions, even trillions, of compounds at a lower cost and faster pace than traditional methods. HitGen has established a robust synthesis process and quality control system for DNA-encoded libraries, allowing for the efficient and high-quality construction of these libraries.)
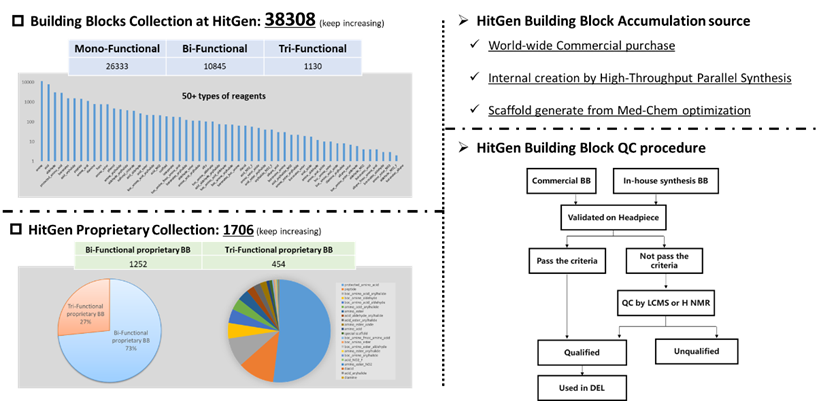
HitGen has amassed a collection of over 40,000 molecular building blocks, with the number and variety of these blocks continuously expanding. Through a stringent quality control system, HitGen's DEL platform has successfully constructed more than one trillion DNA-encoded compounds.
HitGen possesses an automated platform that supports the entire DEL synthesis process. This highly automated DNA-encoded library synthesis platform can accurately and efficiently handle tens of thousands of reactions in parallel, enabling the delivery of DEL products from design to completion within one to three months.


HitGen has independently developed and accumulated over 150 DNA-compatible chemical reactions, providing a solid foundation for the expansion of the diversity and drug-likeness of DEL molecules.


HitGen has established a comprehensive process control and final product quality evaluation system to ensure the high-quality delivery of DEL products.
We use cookies to provide a better web experience.
By using our site, you acknowledge our use of cookies and please read our Cookie Notice for
More information