Get up to date with the latest HitGen articles and join us in the events
Macrocycles1 are generally defined as organic compounds with a ring of at least 12 atoms and hold in a chemical space between small molecules and biologics (Figure 1). With the constrained but somewhat flexible conformation, macrocycles often show higher affinity and selectivity to targets compared with their linear analogues. Therefore, macrocycles constitute an excellent tool for the targets which are difficult to modulate by traditional small molecules. With the enormous structural diversity, many of macrocycles display a wide range of functional capability and remarkable biological activities, which makes them as an important modality in drug discovery. More than 60 macrocycles have been approved as drugs by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration. Most of the macrocyclic drugs are natural products or their derivatives. Infectious disease, oncology, autoimmune disorders, and immunosuppressants are the major therapeutic indications of macrocyclic drugs.
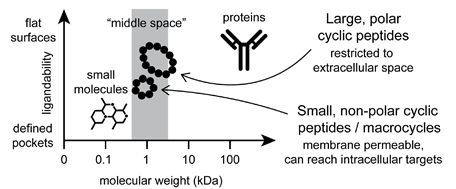
Figure 1. Comparison of macrocycles to small molecules and biologics.1b
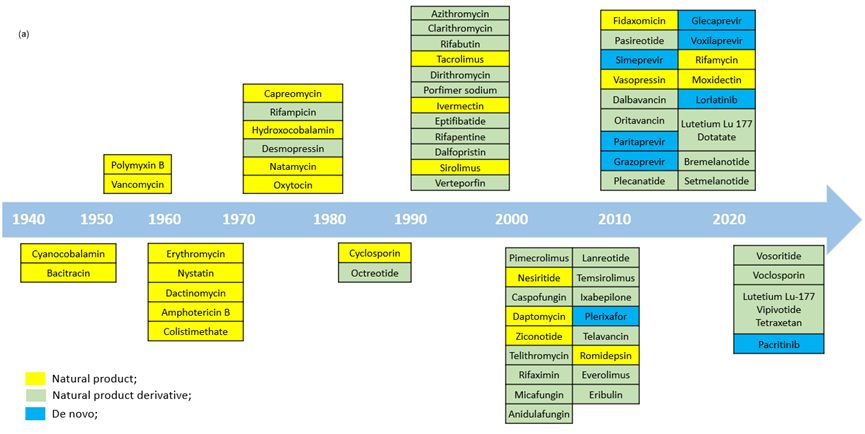
Figure 2. (a) Macrocyclic drugs approved by FDA1a; (b) Examples of macrocycle drug structures.
In addition to being used as drugs, macrocycles have also been widely applied in disease diagnosis and drug delivery2. There are several kinds of payloads, including: (1) Radionucleotides: Lutathera® ([177Lu] Lu-DOTA-TATE) was approved by FDA in 2018 for treating somatostatin inhibitor receptor-positive gastroenteropancreatic neuroendocrine tumors;2c (2) Organic fluorophores: Combination of organic fluorophores and cyclic peptides could generate useful probes for biological assays targeting specific proteins;2d (3) Peptides: Qiu et al. reported cyclic RGD-peptide-functionalized polylipopeptide micelles for enhanced loading and targeted delivery of monomethyl auristatin E;2e (4) Nucleic acids: Hirano et al. reported magainin 2-derived stapled peptides for intracellular delivery of nucleic acids such as pDNA, mRNA, and siRNA.2f
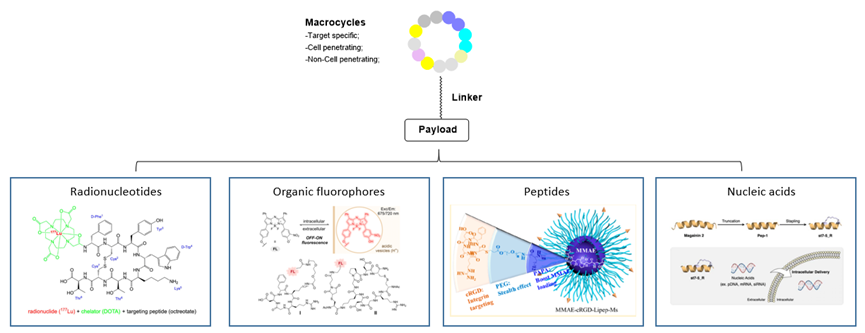
Figure 3. Conjugates with macrocycles.2
Properties of macrocycle drugs
Properties of FDA-approved macrocyclic drugs and clinical candidates have been analyzed.1a Macrocycles usually occupy in chemical space beyond the Rule of 5 (bRo5), but 30-40% of the drugs and clinical candidates are orally bioavailable. Simple models (HBD ≤ 7 in combination with either MW < 1000 Da or cLogP > 2.5) could be used as a first filter to assess whether a macrocycle is oral or parenteral (Figure 4). This analysis will provide the guidance for the design of macrocycles in the future.
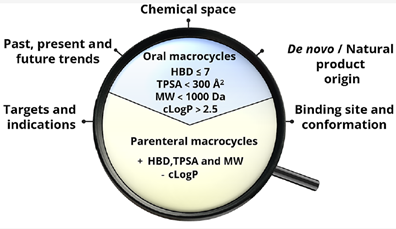
Figure 4. Properties of macrocycle drugs1a
Methodologies for macrocyclic drug discovery.
The discovery of macrocyclic drugs is predominantly stemmed from natural products or their derivatives. However, some of the natural products have the complex structures and are difficult to be synthesized by traditional small molecule chemistry. Therefore, de novo design and synthesis of macrocycles have attracted much attention. With the development of macrocycle synthesis and screening technology, phage display and mRNA display have enabled the de novo discovery of macrocycles. However, both technologies are limited to mostly natural amino acids as building blocks and the restricted monomers limits the overall macrocycle diversity.
As compared to biological display methods, DNA-encoded library technology (DELT)3 can easily incorporate a wide range of unnatural amino acids as building blocks. The combination of unnatural elements and various macrocyclization methods could expand the chemical space and structural diversity of macrocycles. Rational design and building blocks selection could modify the skeleton and side chain of macrocycles, which have the potential to improve the properties of macrocycle molecules generated. In addition to finding ligands to the targets directly, DEL selection can afford much information of enriched macrocycles, which might be a good starting point for pharmacokinetic property optimization to achieve membrane permeation or oral bioavailability. With billions of DNA-tagged macrocycles and high throughput screening, macrocyclic DELs stands out as a practical technology for the discovery of macrocyclic hits. Many macrocyclic binders against various targets have been discovered by DELT (Figure 5).
Figure 5. Examples of discovered macrocyclic hits from DELT3
HitGen Macrocyclic DELs
High-quality of macrocyclic DELs with different ring sizes have been designed and synthesized at HitGen (Figure 6) and this ready-made macrocyclic DELs collection can be directly used for target screening. Key features of macrocyclic DELs at HitGen are:
Ø Library size: >40 Bn compounds;
Ø Diversity of building blocks: >500 natural and unnatural amino acids and >300 di/tri/tetra-peptides;
Ø Peptide length within rings: 2-13 amino acids;
Ø Introducing of special amino acids including N-methyl building blocks and lipophilic side chain to modify properties of macrocycles such as MW, LogP, HBA/HBD etc.
Ø Macrocyclization strategy: click chemistry, thioether formation, disulfide formation and other novel cyclization methods.
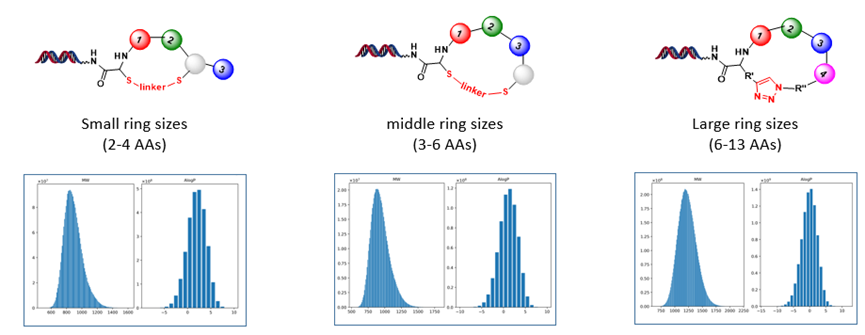
Figure 6. Macrocyclic DELs at HitGen.
Application of macrocyclic DELs
HitGen has rich experiences in macrocyclic DEL selection. Our macrocyclic DELs has been used for various targets screening. A successful selection case of macrocyclic DELs are showed in Figure 7.
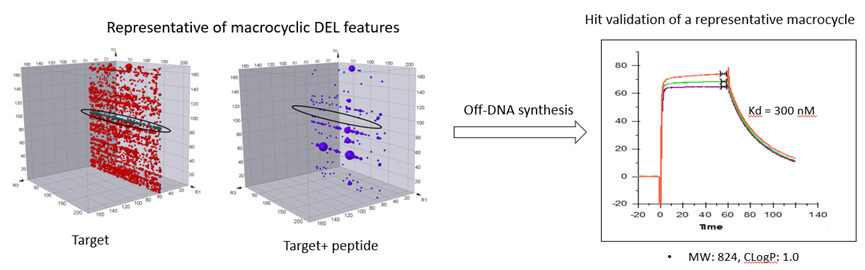
Figure 7. Macrocyclic DEL selection results and hit validation.
In addition to finding macrocyclic lead compounds directly, the macrocyclic DEL could be a good starting point for transporting cargos including small molecules, antibody, nucleic acids etc. (Figure 8).
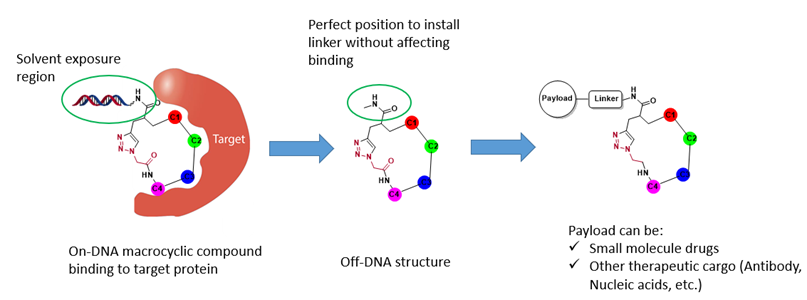
Figure 8. Application of macrocyclic DELs for delivery system.
HitGen PCP Platform
By integration of parallel peptide synthesis, peptide DEL construction and screening etc., HitGen has established a comprehensive peptide-conjugate platform (PCP) (Figure 9). This platform can provide the synthesis of specific amino acids/peptides (used for DEL library design and build), peptide conjugates synthesis (validation of activity before/after DEL selection), peptide DEL design and construction, DEL selection and high throughput off-DNA synthesis of peptides.
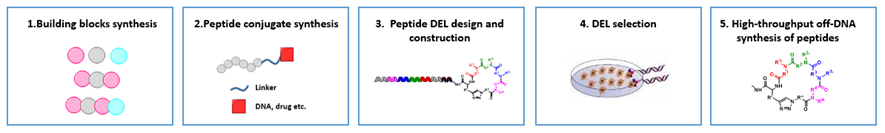
Figure 9. HitGen PCP Platform
HitGen services include:
Ø Custom macrocyclic/linear peptide DEL build;
Ø >40 Bn macrocyclic DELs for selection of targets;
Ø High throughput off-DNA synthesis of peptides;
Ø Synthesis of macrocyclic/linear peptide conjugates.
Reference:
[1] (a) Jimenez, D. G.; Poongavanam, V.; Kihlberg, J. Macrocycles in Drug Discovery-Learning from the Past for the Future. J. Med. Chem. 2023, 66, 5377. (b) Ji, X.; Nielsen, A. L.; Heinis, C. Cyclic peptides for drug development. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2024, 63, e202308251.
[2] (a) Gong, L.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Y.; Wu, H.; Liu, C.; Chang, S.; Chen, L.; Jin, M.; Wang, Q.; Gao, Z.; Huang, W. Research advances in peptide–drug conjugates. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B, 2023, 13, 3659. (b) Cooper, B. M.; Iegre, J.; O’ Donovan, D. H.; Halvarsson, M. Ӧ.; Spring, D. R. Peptides as a platform for targeted therapeutics for cancer: peptide–drug conjugates (PDCs). Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 1480. (c) Hennrich, U.; Kopka, K. Lutathera®: The First FDA- and EMA-Approved Radiopharmaceutical for Peptide Receptor Radionuclide Therapy. Pharmaceuticals 2019, 12, 114. (d) Mendive-Tapia, L.; Wang, J.; Vendrell, M. Fluorescent cyclic peptides for cell imaging. Peptide Science 2021, 113, e24181. (e) Qiu, M.; Wang, X.; Sun, H.; Zhang, J.; Deng, C.; Zhong, Z. Cyclic RGD-Peptide-Functionalized Polylipopeptide Micelles for Enhanced Loading and Targeted Delivery of Monomethyl Auristatin E. Mol. Pharmaceutics 2018, 15, 4854. (f) Hirano, M.; Yokoo, H.; Goto, C.; Oba, M.; Misawa, T.; Demizu, Y. Magainin 2-derived stapled peptides derived with the ability to deliver pDNA, mRNA, and siRNA into cells. Chem. Sci. 2023, 14, 10403.
[3] Plais, L.; Scheuermann, J. Macrocyclic DNA-encoded chemical libraries: a historical perspective. RSC Chem. Biol. 2022, 3, 7.
We use cookies to provide a better web experience.
By using our site, you acknowledge our use of cookies and please read our Cookie Notice for
More information